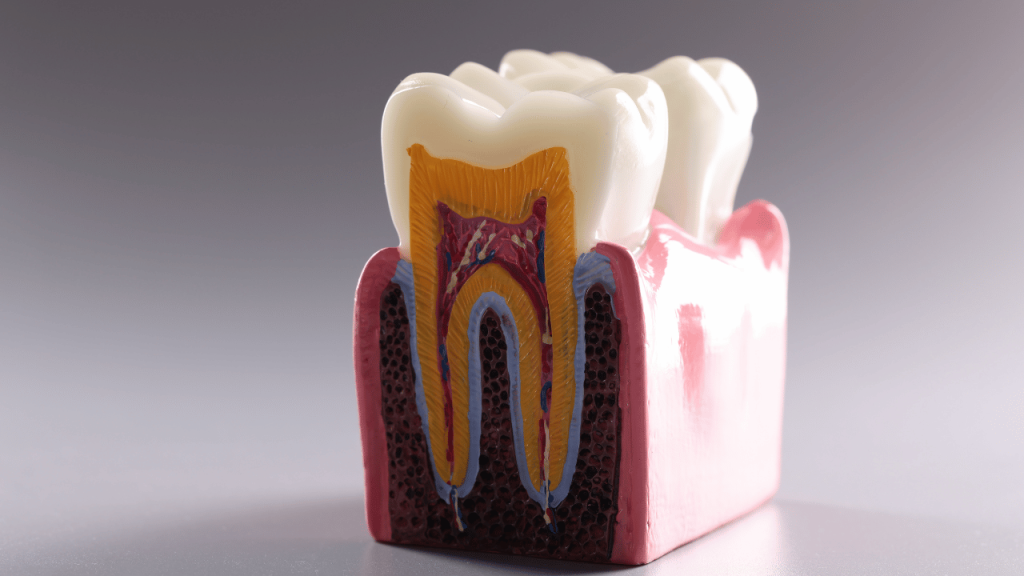
Understanding what teeth are made of is essential to maintaining good dental health. Teeth are complex structures that are composed of different parts, each with its own unique function. From the hard outer enamel to the soft inner pulp, each part of the tooth plays a critical role in the overall structure and function of the tooth.
With over a decade of experience as a dentist, notes, “Understanding the composition of teeth is important because it helps us understand how to take care of them.” By knowing what teeth are made of and how they function, we can take steps to maintain good oral hygiene and prevent common dental problems such as cavities, gum disease, and tooth decay.
So, what are teeth made of? Let’s take a closer look at the different parts of the human tooth and their composition.
Key Takeaways
- Teeth are complex structures made up of different parts, each with its own unique function.
- Understanding the composition of teeth is essential to maintaining good dental health.
- By knowing what teeth are made of and how they function, we can take steps to prevent common dental problems.
Parts of the Human Tooth
Teeth are complex structures that play a crucial role in chewing, speaking, and aesthetics. They are made up of several different parts that work together to provide function and protection.
Crown
The crown is the visible part of the tooth that protrudes above the gum line. It is covered by a layer of enamel, which is the hardest substance in the human body. Enamel is made up of hydroxyapatite crystals, which provide strength and protection against mechanical stress and chemical erosion. The crown is responsible for biting and grinding food, and it also plays an important role in aesthetics.
Root
The root is the part of the tooth that is embedded in the jawbone and holds the tooth in place. It is covered by a layer of cementum, which anchors the tooth to the periodontal ligament. The root is made up of dentin, which is a softer and more porous material than enamel. Dentin contains dentinal tubules, which are tiny channels that connect the pulp cavity to the surface of the tooth. The root is responsible for providing support and stability to the tooth.
Neck
The neck is the part of the tooth that connects the crown and the root. It is covered by the gums, also known as the gingiva. The gums are made up of soft tissue that protects the tooth and provides a seal around it. The junction between the gum and the tooth is called the gingival sulcus, which is an important site for defense against dental caries and other infections.
Pulp
The pulp is the soft tissue that fills the pulp cavity inside the tooth. It contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue, which are responsible for providing nutrition and sensation to the tooth. The pulp is surrounded by dentin, which provides protection against mechanical stress and bacterial invasion. The pulp is also the site of the root canal, which is a common treatment for dental caries and other infections.
In summary, the human tooth is a complex structure that is made up of several different parts. These parts work together to provide function and protection, and they are essential for maintaining oral health and overall well-being.
Human Tooth – Sections and Composition
Have you ever wondered what your teeth are made of? Teeth are fascinating structures that are composed of multiple layers of both hard and soft tissue. Let’s take a closer look at the sections and composition of a human tooth.
Enamel
Enamel is the outermost layer of the tooth and is the hardest substance in the human body. It is a translucent, mineralized substance that covers the crown of the tooth. Enamel is composed of 96% mineral, primarily hydroxyapatite, and 4% organic material and water. It helps protect the tooth from wear and tear, and from damage caused by bacteria and acid.
Dentin
Dentin is the layer of the tooth that lies beneath the enamel. It is softer than enamel and is composed of mineralized tissue, collagen [1], and water. Dentin is responsible for the color of the tooth and provides support to the enamel. It also contains microscopic tubules that connect to the pulp, allowing for the transmission of sensory information, such as temperature and pain.
Pulp
The pulp is the soft tissue at the center of the tooth that contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. It is responsible for the formation and development of the tooth, and for maintaining its vitality. The pulp can become inflamed or infected as a result of dental caries or trauma, which can cause pain and sensitivity. In some cases, a root canal may be necessary to remove the infected pulp and save the tooth.
Cementum
Cementum is a layer of hard, mineralized tissue that covers the root of the tooth. It helps anchor the tooth to the surrounding bone and provides a surface for the attachment of the periodontal ligament. Cementum is composed of mineralized tissue, collagen, and water.
In conclusion, the human tooth is a complex and fascinating structure that is composed of multiple layers of both hard and soft tissue. Understanding the sections and composition of the tooth can help us better appreciate the importance of dental hygiene and care.
Enamel
Have you ever wondered why your teeth are so hard? The answer lies in the enamel, which is the hardest substance in the human body. Enamel is the outermost layer of the tooth crown, and it serves as the first line of defense against physical and chemical damage. It also plays a significant role in the aesthetics of your teeth.
Despite being incredibly durable, enamel is vulnerable to decay. That’s why it’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene and use fluoride toothpaste to keep your enamel strong. Fluoride helps to demineralize the enamel, making it stronger and more resistant to decay [2].
Composition of Enamel
Enamel is a highly mineralized substance, consisting mainly of hydroxyapatite, a calcium phosphate mineral [3]. However, it also contains magnesium, sodium, fluoride, and carbonate. The mineral content of enamel makes it incredibly hard and durable.
Enamel is formed by specialized cells called ameloblasts, which produce and secrete the enamel matrix. The enamel matrix is composed of proteins and minerals, which are organized into a highly ordered structure. As the enamel matrix is secreted, the ameloblasts move away from the enamel surface, leaving behind a fully mineralized layer of enamel.
In summary, enamel is the hard, outer layer of the tooth crown that protects against physical and chemical damage. It is composed mainly of hydroxyapatite and other minerals, and it is formed by specialized cells called ameloblasts. To keep your enamel strong, maintain good oral hygiene and use fluoride toothpaste.
Dentin
Dentin is the secondary support layer of the tooth, sandwiched between the outer enamel and the inner pulp. It is a hard, calcified tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth. Dentin is composed of hydroxyapatite crystals, which are similar to those found in enamel, but are arranged differently.
Dentin is a living tissue that contains tiny channels called dentinal tubules, which are filled with fluid and extend from the pulp to the outer surface of the dentin. These tubules are lined with cells called odontoblasts [4], which are responsible for the formation of dentin. The odontoblasts also play a role in the sensation of the tooth, as they are connected to nerve fibers in the pulp.
One of the key functions of dentin is to protect the pulp from temperature changes and other external stimuli. Dentin is a good insulator, and it helps to shield the pulp from sudden temperature changes that could cause pain or damage. Dentin is also able to respond to temperature changes by expanding and contracting, which helps to maintain the structural integrity of the tooth.
Overall, dentin is an important component of dental anatomy, providing resilience and capacity for sensation. Its unique composition and structure make it a critical component of the tooth, helping to protect the pulp and maintain the overall health of the tooth.
Cementum
Cementum is a thin layer of calcified tissue that covers the root of a tooth and helps to anchor it to the jawbone. It is a unique tissue that differs in composition from enamel and dentin. Unlike enamel, which is the hardest substance in the body, and dentin, which is a bone-like substance, cementum is softer and more porous. Cementum is a dynamic entity within the periodontium, which is the supporting structure of the teeth.
Cementum plays a crucial role in anchoring the tooth and supporting its stability. It is attached to the alveolar bone by the fibers of the periodontal ligament and to the soft tissues of the gum by the gingival fibers. The periodontal ligament is a specialized connective tissue that surrounds the root of the tooth and helps to cushion it against the forces of biting and chewing. The gingival fibers are a network of collagen fibers that attach the gums to the teeth.
Cementum is also important in protecting the root of the tooth from dental caries, which is a bacterial infection that can cause decay and damage to the tooth. Cementum is more resistant to acid than enamel and dentin, which makes it less susceptible to decay. However, if the cementum is exposed due to gum recession or other factors, it can be eroded by the acid produced by the bacteria, leading to root caries.
In conclusion, cementum is a vital component of the teeth that helps to anchor them to the jawbone and support their stability. Its unique composition compared to enamel and dentin makes it more resistant to decay, but it can still be eroded by acid if exposed.
Pulp
Have you ever wondered what the inside of your tooth looks like? The pulp is the soft, living tissue that is located in the center of your tooth. It is made up of blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. This tissue is responsible for the tooth’s vitality and response to stimuli.
The pulp is located in the pulp cavity, which is situated in the center of the tooth. The pulp cavity is connected to the pulp chamber, which is located in the crown of the tooth. The pulp chamber is surrounded by dentin, which is the hard, calcified tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth.
The pulp is made up of several different types of cells, including fibroblasts [5] and macrophages [6]. Fibroblasts are responsible for producing the collagen fibers that make up the connective tissue in the pulp. Macrophages are responsible for removing dead or damaged cells from the pulp.
The pulp is also home to the tooth’s nerves and blood vessels. The nerves in the pulp are responsible for transmitting signals to the brain, which allows us to feel sensations like hot and cold. The blood vessels in the pulp are responsible for supplying the tooth with oxygen and nutrients.
Unfortunately, trauma and decay can have a negative impact on the health of the pulp. If the pulp becomes damaged or infected, it can cause a lot of pain and discomfort. In some cases, a root canal may be necessary to remove the damaged pulp and save the tooth.
Overall, the pulp plays a critical role in the health and vitality of your teeth. By taking good care of your teeth and practicing good oral hygiene, you can help keep your pulp healthy and avoid any unnecessary pain or discomfort.
Frequently Asked Questions
What substances contribute to the composition of tooth enamel?
Tooth enamel is primarily composed of hydroxyapatite, a mineral made up of calcium and phosphate ions. This mineral makes enamel the hardest substance in the human body. Other substances that contribute to enamel include water, organic material, and trace amounts of other minerals such as fluoride.
How does the mineral content of teeth compare to that of bones?
While teeth and bones both contain minerals such as calcium and phosphate, the mineral content of teeth is much higher than that of bones. Teeth are made up of around 96% mineral, while bones are only around 70% mineral. This high mineral content is what gives teeth their strength and durability.
What materials are typically used in the creation of dental prosthetics?
Dental prosthetics, such as dentures, are typically made from materials such as acrylic resin, porcelain, or a combination of the two. These materials are chosen for their durability, strength, and ability to mimic the appearance of natural teeth.
Can you explain the role of keratin in the structure of teeth?
Keratin is a protein that is found in the outer layer of skin, hair, and nails. While keratin is not a major component of teeth, it does play a role in the formation of tooth enamel. Specifically, keratin helps to regulate the growth and development of enamel-forming cells called ameloblasts.
In what ways are human teeth different from ivory?
Human teeth and ivory are both made up of similar materials, such as hydroxyapatite and collagen. However, there are some key differences between the two. For example, human teeth are more complex in their structure and are made up of several different layers, while ivory is a simpler structure. Additionally, human teeth are living tissue, while ivory is not.
Are there any similarities between teeth and cartilage in their makeup?
While teeth and cartilage are both made up of collagen, they differ in their mineral content. Teeth are primarily composed of hydroxyapatite, while cartilage does not contain any mineralized tissue. Additionally, teeth are a hard, durable structure, while cartilage is a softer, more flexible tissue.

